Compare Strategies
| LONG PUT | LONG GUTS | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| About Strategy |
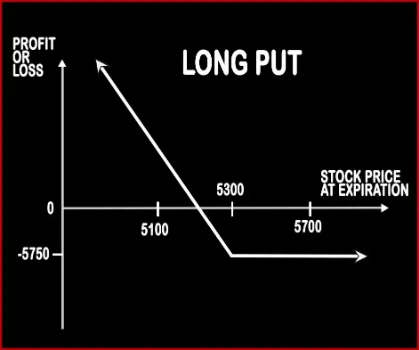
Long Put Option StrategyThis strategy is implemented by buying 1 Put Option i.e. a single position, when the person is bearish on the market and expects the market to move downwards in the near future. |
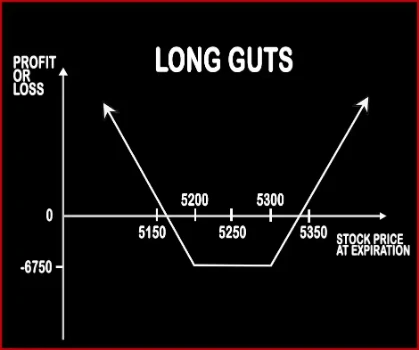
Long Guts Option StrategyThis strategy is implemented by a trader when he is neutral on the movements and bullish on volatility i.e. he expects the stock to move in either direction with high magnitude. This strategy involves buying 1 ITM Call Option and 1 ITM Put Option. This strategy can be called as Debit Spread because trader’s account is debited at the time of entering the positions.< .. |
LONG PUT Vs LONG GUTS - Details
| LONG PUT | LONG GUTS | |
|---|---|---|
| Market View | Bearish | Neutral |
| Type (CE/PE) | PE (Put Option) | CE (Call Option) + PE (Put Option) |
| Number Of Positions | 1 | 2 |
| Strategy Level | Beginners | Beginners |
| Reward Profile | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| Risk Profile | Limited | Limited |
| Breakeven Point | Strike Price of Long Put - Premium Paid | Upper Breakeven Point = Net Premium Paid + Strike Price of Long Call, Lower Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Long Put - Net Premium Paid |
LONG PUT Vs LONG GUTS - When & How to use ?
| LONG PUT | LONG GUTS | |
|---|---|---|
| Market View | Bearish | Neutral |
| When to use? | A long put option strategy works well when you're expecting the underlying asset to sharply decline or be volatile in near future. | This strategy is implemented by a trader when he is neutral on the movements and bullish on volatility i.e. he expects the stock to move in either direction with high magnitude. |
| Action | Buy Put Option | Buy 1 ITM Call, Buy 1 ITM Put |
| Breakeven Point | Strike Price of Long Put - Premium Paid | Upper Breakeven Point = Net Premium Paid + Strike Price of Long Call, Lower Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Long Put - Net Premium Paid |
LONG PUT Vs LONG GUTS - Risk & Reward
| LONG PUT | LONG GUTS | |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Profit Scenario | Profit = Strike Price of Long Put - Premium Paid | Price of Underlying - Strike Price of Long Call - Net Premium Paid OR Strike Price of Long Put - Price of Underlying - Premium Paid |
| Maximum Loss Scenario | Max Loss = Premium Paid + Commissions Paid | Net Premium Paid + Strike Price of Long Put - Strike Price of Long Call + Commissions Paid |
| Risk | Limited | Limited |
| Reward | Unlimited | Unlimited |
LONG PUT Vs LONG GUTS - Strategy Pros & Cons
| LONG PUT | LONG GUTS | |
|---|---|---|
| Similar Strategies | Protective Call, Short Put | Short Put Ladder, Strip, Strap |
| Disadvantage | • 100% loss if strike price, expiration dates or underlying stocks are badly chosen. • Time decay. | • More commission involved than simply buying call or put option. • Expensive. |
| Advantages | • Limited risk to the premium paid. • Less capital investment and more profit. • Unlimited profit potential with limited risk. | • Investors can get unlimited profit if the underlying asset goes up or down. • Ability to profit no matter if the market goes in either direction. • Limited loss. |