Compare Strategies
| RATIO CALL SPREAD | SHORT STRADDLE | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| About Strategy |
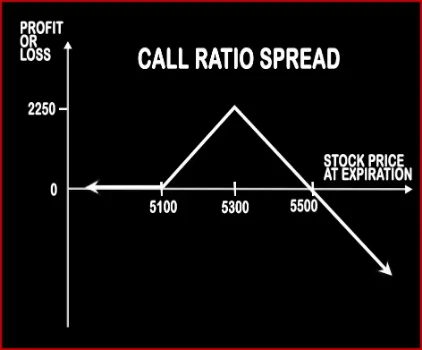
Ratio Call Spread Option StrategyAs the name suggests, a ratio of 2:1 is followed i.e. buy 1 ITM Call and simultaneously sell OTM Calls double the number of ITM Calls (In this case 2). This strategy is used by trader who is neutral on the market and bearish on the volatility in the near future. Here profits will be capped up to the premium amount and risk will be potentially unlimited since he is |
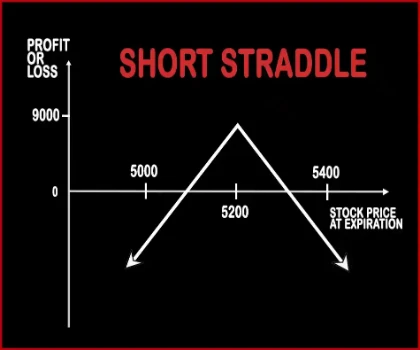
Short Straddle Option strategyThis strategy is just the opposite of Long Straddle. A trader should adopt this strategy when he expects less volatility in the near future. Here, a trader will sell one Call Option & one Put Option of the same strike price, same expiry date and of the same underlying asset. If the stock/index hovers around the same levels then both the options will expire worthless an .. |
RATIO CALL SPREAD Vs SHORT STRADDLE - Details
| RATIO CALL SPREAD | SHORT STRADDLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Market View | Neutral | Neutral |
| Type (CE/PE) | CE (Call Option) | CE (Call Option) + PE (Put Option) |
| Number Of Positions | 3 | 2 |
| Strategy Level | Beginners | Advance |
| Reward Profile | Limited | Limited |
| Risk Profile | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| Breakeven Point | Upper Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Short Calls + (Points of Maximum Profit / Number of Uncovered Calls), Lower Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Long Call +/- Net Premium Paid or Received | Lower Breakeven = Strike Price of Put - Net Premium, Upper breakeven = Strike Price of Call+ Net Premium |
RATIO CALL SPREAD Vs SHORT STRADDLE - When & How to use ?
| RATIO CALL SPREAD | SHORT STRADDLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Market View | Neutral | Neutral |
| When to use? | This strategy is used by trader who is neutral on the market and bearish on the volatility in the near future. Here profits will be capped up to the premium amount and risk will be potentially unlimited since he is selling two calls. | This strategy is work well when an investor expect a flat market in the coming days with very less movement in the prices of underlying asset. |
| Action | Buy 1 ITM Call, Sell 2 OTM Calls | Sell Call Option, Sell Put Option |
| Breakeven Point | Upper Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Short Calls + (Points of Maximum Profit / Number of Uncovered Calls), Lower Breakeven Point = Strike Price of Long Call +/- Net Premium Paid or Received | Lower Breakeven = Strike Price of Put - Net Premium, Upper breakeven = Strike Price of Call+ Net Premium |
RATIO CALL SPREAD Vs SHORT STRADDLE - Risk & Reward
| RATIO CALL SPREAD | SHORT STRADDLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Profit Scenario | Strike Price of Short Call - Strike Price of Long Call + Net Premium Received - Commissions Paid | Max Profit = Net Premium Received - Commissions Paid |
| Maximum Loss Scenario | Price of Underlying - Strike Price of Short Calls - Max Profit + Commissions Paid | Maximum Loss = Long Call Strike Price - Short Call Strike Price - Net Premium Received |
| Risk | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| Reward | Limited | Limited |
RATIO CALL SPREAD Vs SHORT STRADDLE - Strategy Pros & Cons
| RATIO CALL SPREAD | SHORT STRADDLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Similar Strategies | Variable Ratio Write | Short Strangle |
| Disadvantage | • Unlimited potential loss. • Complex strategy with limited profit. | • Unlimited risk. • If the price of the underlying asset moves in either direction then huge losses can occur. |
| Advantages | • Downside risk is almost zero. • Investors can book profit from share prices moving within given limits. • Trader can maximise profit when the share closes at the upper breakeven point. | • A trader can earn profit even when there is no volatility in the market . • Allows you to benefit from double time decay. • Trader can collect premium from puts and calls option . |