Compare Strategies
| LONG CALL | SHORT STRADDLE | |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| About Strategy |
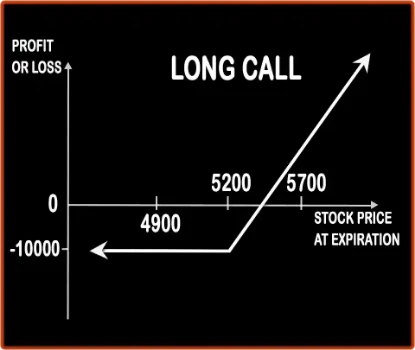
Long Call Option StrategyThis is one of the basic strategies as it involves entering into one position i.e. buying the Call Option only. Any investor who buys the Call Option will be bullish in nature and would be expecting the market to give decent returns in the near future. Risk:
|
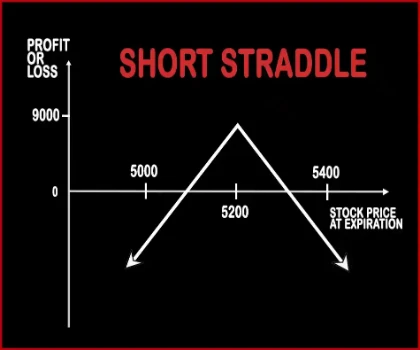
Short Straddle Option strategyThis strategy is just the opposite of Long Straddle. A trader should adopt this strategy when he expects less volatility in the near future. Here, a trader will sell one Call Option & one Put Option of the same strike price, same expiry date and of the same underlying asset. If the stock/index hovers around the same levels then both the options will expire worthless an .. |
LONG CALL Vs SHORT STRADDLE - Details
| LONG CALL | SHORT STRADDLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Market View | Bullish | Neutral |
| Type (CE/PE) | CE (Call Option) | CE (Call Option) + PE (Put Option) |
| Number Of Positions | 1 | 2 |
| Strategy Level | Beginner Level | Advance |
| Reward Profile | Unlimited | Limited |
| Risk Profile | Limited | Unlimited |
| Breakeven Point | Strike Price + Premium | Lower Breakeven = Strike Price of Put - Net Premium, Upper breakeven = Strike Price of Call+ Net Premium |
LONG CALL Vs SHORT STRADDLE - When & How to use ?
| LONG CALL | SHORT STRADDLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Market View | Bullish (Any investor who buys the Call Option will be bullish in nature and would be expecting the market to give decent returns in the near future.) | Neutral |
| When to use? | This strategy work when an investor expect the underlying instrument move in upward direction. | This strategy is work well when an investor expect a flat market in the coming days with very less movement in the prices of underlying asset. |
| Action | Buying Call option | Sell Call Option, Sell Put Option |
| Breakeven Point | Strike price + Premium | Lower Breakeven = Strike Price of Put - Net Premium, Upper breakeven = Strike Price of Call+ Net Premium |
LONG CALL Vs SHORT STRADDLE - Risk & Reward
| LONG CALL | SHORT STRADDLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Profit Scenario | Underlying Asset close above from the strike price on expiry. | Max Profit = Net Premium Received - Commissions Paid |
| Maximum Loss Scenario | Premium Paid | Maximum Loss = Long Call Strike Price - Short Call Strike Price - Net Premium Received |
| Risk | Limited | Unlimited |
| Reward | Unlimited | Limited |
LONG CALL Vs SHORT STRADDLE - Strategy Pros & Cons
| LONG CALL | SHORT STRADDLE | |
|---|---|---|
| Similar Strategies | Protective Put | Short Strangle |
| Disadvantage | • In this strategy, there is not protection against the underlying stock falling in value. • 100% loss if the strike price, expiration dates or underlying stocks are badly chosen. | • Unlimited risk. • If the price of the underlying asset moves in either direction then huge losses can occur. |
| Advantages | • Less investment, more profit. • Unlimited profit with limited risk. • High leverage than simply owning the stock. | • A trader can earn profit even when there is no volatility in the market . • Allows you to benefit from double time decay. • Trader can collect premium from puts and calls option . |